Colonialism and Imperialism in literature talked about the themes, impacts, and actions of dominant powers exerting control over other nations and cultures. It’s aim to shaping narratives of power, resistance, and identity within literary works.
The practice of one nation controlling and exploiting other nations by establishing power and exerting authority.
While Imperialism is the extension of a nation’s power and influence over other empires, often through economic, political, or cultural means.

Basic Concepts Of Colonialism And Imperialism
Colonialism
Territorial Expansion
Focus: Colonialism shows powerful nations physically taking over other lands and means of earning by force. They do just for setting up colonies where their people settle.
Direct Control
- Hands-On Approach: Those in charge from the powerful country directly run the colonies, making laws, and ensuring their rules are followed.
- Resource Exploitation: They take resources or means of earning from these colonies, using the land’s wealth and the work of the locals to benefit themselves.
Historical Context
- Age of Exploration: This happened during a time when countries like Europe explored and claimed new territories globally, seeking wealth and power.
- Impact on Indigenous Cultures: Impact on indigenous cultures means the colonizers forced their language, education, and laws on the locals, often erasing or changing the native traditions and ways of life.
Imperialism
Diverse Forms of Control
- Not Just Land Takeovers: Imperialism is not only about physically taking over lands. It is about controlling others’ economies, politics, or cultures too.
- Economic Influence: Strong countries control resources, trade routes, and markets of weaker nations, affecting global economies.
Indirect Influence
- Control Without Settling: Powerful nations can control or influence others without living there, using money, ideas, or politics.
- Political Maneuvering: They might affect how other countries run things by playing politics or getting involved in their decision-making.
Historical Roots
- Ancient Origins: The idea goes back to ancient empires like Rome or Greece, where mighty nations controlled other regions by force or agreements.
- Impact on Indigenous Cultures: Unlike colonizers who imposed their ways directly, imperialist influence made locals adopt new things, sometimes blending with their culture rather than completely changing or destroying it.
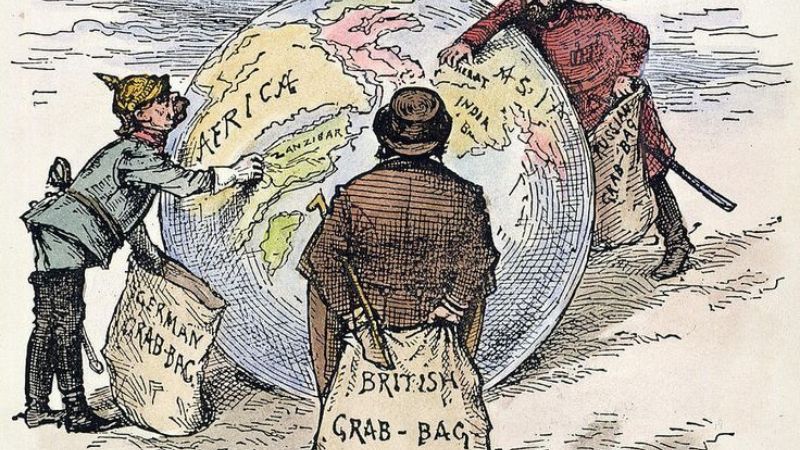
Imperialism and Colonialism In Literary works
Literary works of art such as The Tempest and Heart of Darkness powerfully examine imperialism and colonialism. Early themes of colonization, dominance, and the civilizing mission are reflected in Prospero’s rule over Caliban and the island in The Tempest.
Heart of Darkness delves deeply into the atrocities of European imperialism in Africa, revealing the cruelty, greed, and moral decay concealed beneath pretenses of advancement.
The intricacies of resistance, identity, and power are exposed in both pieces. They expose the effects on indigenous cultures and argue the claims of empire through narrative and symbolism. As a result, literature becomes a forum for going over and critiquing colonial practices.
Similarities Between Imperialism and Colonialism
Imperialism and colonialism, while different, share fundamental similarities in their historical roots and control over foreign nations. Exploring these similarities provides insights into their interconnectedness and impact on global history.
Territorial Domination
Both imperialism and colonialism involve powerful nations extending their control beyond their areas. While colonialism directly establishes colonies through settlements, imperialism seeks influence through different means without always establishing physical settlements.
Resource Exploitation
In both, resource exploitation is a common feature. Colonialism involves direct extraction of resources from colonies for the benefit of the colonizing nation. Similarly, imperialism often involves controlling resources and trade routes for economic gain.

Historical Context
Both concepts emerged from historical periods when dominant powers sought expansion. Colonialism surged during the Age of Exploration (16th-20th centuries), while imperialism spans ancient civilizations to modern times, reflecting a continuous pursuit of power and dominance.
Cultural Impact
Both exerted significant cultural influence. While colonialism directly imposed its culture, language, and laws on colonies, imperialism, through economic and political control, also led to the adoption of foreign customs, languages, or institutions in colonized regions.
Global Influence
Imperialism and colonialism impacted global geopolitics, shaping economies, politics, and societies worldwide. In addition, they left enduring legacies, contributing to the complexities of our modern world.
Characteristics Of Imperialism And Colonialism
| Characteristics | Imperialism | Colonialism |
| Territorial Control | Extending influence over regions without direct colonies | Direct establishment of colonies in foreign territories |
| Resource Exploitation | Control and exploitation of resources for economic gain | Extraction and utilization of resources from colonies for benefit |
| Cultural Influence | Spreading cultural ideas, norms, or practices indirectly | Imposing the colonizers’ culture and language directly |
| Methods of Control | Using economic, political, or military means for dominance | Direct rule through appointed administrators and laws |
| Historical Context | Rooted in various historical eras and civilizations | Emerged significantly during the Age of Exploration |
FAQs
A colony is a specific territory controlled by a dominant country, while an empire is a group of territories or countries ruled by a powerful nation.
No, imperialism is not always colonialism; imperialism encompasses various ways a powerful country extends control over others. While colonialism specifically involves establishing colonies in foreign lands.
The main colonists historically were countries like Britain, France, Spain, Portugal, and the Netherlands, among others, which established colonies around the world.
The main imperialist nations historically are the countries like Britain, France, Germany, Japan, and the United States, which sought to extend their influence and control over other regions through various means such as economic, political, or military dominance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, colonialism and imperialism are powerful forces that shaped global history and literature by highlighting domination, resistance, and identity. Colonialism involved direct territorial control and settlement, while imperialism extended influence through political, economic, and cultural means. Both disrupted indigenous lives and reshaped societies, leaving lasting impacts seen in literary narratives and historical memory.









